UK heatwaves 2022: is hot weather caused by climate change - as Met Office lifts temperature thresholds
and live on Freeview channel 276
The Met Office is increasing the heatwave temperature threshold across eight English counties before the summer as the climate continues to warm.
A heatwave is classed relative to the current climate, and average temperatures are creeping up due to global warming.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdFor weather to be considered a heatwave, the temperature in a specific area has to reach a threshold set by the Met Office for three consecutive days - which varies by UK county.
In parts of England, hot summer days will now have to reach 28C to be declared a heatwave.
Here is where the heatwave threshold is changing in England and whether warming temperatures are caused by climate change.
Where is the heatwave threshold increasing?
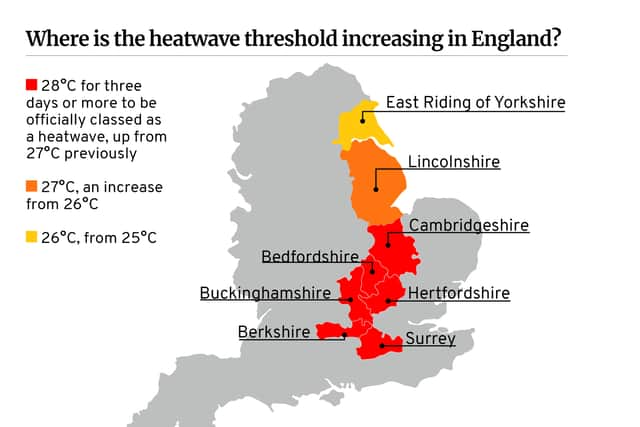

The three-day temperature threshold for a heatwave is jumping from 27C to 28C in six counties.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThese counties are Surrey, Berkshire, Buckinghamshire, Bedfordshire, Hertfordshire and Cambridgeshire.
In Lincolnshire, temperatures will have to reach 27C instead of 26C for three days to be determined a heatwave.
In the East Riding of Yorkshire, there is now a 26C threshold - up from 25C.
Are warmer temperatures caused by climate change?
The Met Office said its data revealed an "undeniable warming trend for the UK".
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThe greatest temperature rise of more than 1C has been recorded across parts of central and eastern England.
Further north, areas of Scotland and Northern Ireland have seen temperatures rise by around 0.7C.
Dr Mark McCarthy, head of the Met Office National Climate Information Centre, said: "Although heatwaves are extreme weather events, research shows that climate change is making these events more likely.”
Are heatwaves becoming more frequent in the UK?
A Met Office study into the Summer 2018 heatwave in the UK showed that it was 30 times more likely for a heatwave to occur now than in 1750.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThis is because of the higher concentration of carbon dioxide, a climate-heating greenhouse gas, in the atmosphere.
Dr McCarthy added that as these concentrations increase, heatwaves of similar intensity "are projected to become even more frequent, perhaps occurring as regularly as every other year.”


The weather body calculates heatwave thresholds from historical data, previously on the period 1981-2010.
The new limits are based on data from 1991-2020.
Heatwave thresholds are different to extreme heat warnings, which highlight very high temperatures to help protect lives and property.
The 2018 heatwave caused widespread drought, hosepipe bans, crop failures, and a number of wildfires in the UK.
Nearly 700 more deaths than average were recorded during the heatwave’s peak.
Comment Guidelines
National World encourages reader discussion on our stories. User feedback, insights and back-and-forth exchanges add a rich layer of context to reporting. Please review our Community Guidelines before commenting.
