What does far right mean in politics? What Le Pen stands for in France elections and political scale explained
and live on Freeview channel 276
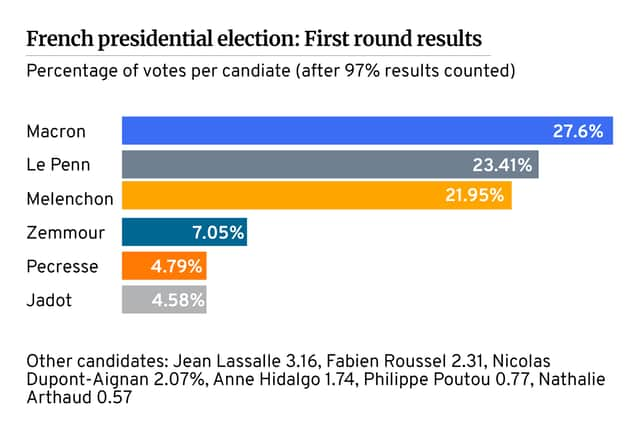
French voters await 24 April for the final round of the country’s presidential elections where President Emmanuel Macron and far-right candidate Marine Le Pen will face each other.
Le Pen came second in the first round, just three points behind Macron.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdPolls suggest the final round will be a very tight contest, with right and potentially even some far-left voters casting ballots for Le Pen.
Her party is positioned on the far-right of the political scale - but what does far right mean in politics and what does Le Pen stand for in France?
What does far right mean in politics?
In politics, ‘right’ voters tend to have a strong sense of national and cultural identity but those on the ‘far right’ go even further than this.
Far right encompasses rejecting the idea of diversity, and perceiving integration with other cultures as a threat to the sense of identity.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThey see those of different races or cultures as outsiders of their country which can lead to unrest within communities and prejudicial attitudes.
The far right appeals to a sense of elitism, with emphasis on the fact that a ‘superior’ community is being eradicated.
We have seen this throughout history with the persecution of people of colour, homosexuals, Jews, Muslims and other minority groups.
What does Le Pen stand for in France?
Marine Le Pen is the leader of France’s National Rally party, formerly known as National Front, which revolves around an anti-immigration and anti-European Union platform.


Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdSome of its members are often being accused of racism and Islamophobia.
In recent years Le Pen’s themes of concerns over insecurity and crime, a feeling of decline and social inequality, and linking those issues to immigration and a perceived threat of Islamism, have taken up space in the public debate arena.
Le Pen has previously described Britain’s vote for Brexit as the most important event since the fall of the Berlin Wall, and Donald Trump’s US presidential victory as "an additional stone in the building of a new world".
In this presidential election, she has promised a referendum on immigration and a rewrite of the constitution to ensure “France for the French” — where native French people would be prioritised over non-French people for welfare benefits, housing, jobs and healthcare.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThe Muslim headscarf, was called “a uniform of totalitarian ideology” by Le Pen and would be banned from the streets and all public places.
She has also focused on the cost of living crisis, promising to cut taxes and waive income tax for under-30s.
Despite being positioned on the far right of the political scale, she seeks to attract working-class voters from both the right and the left.
Other far right candidates, Éric Zemmour and Marion Maréchal, reject this tactic and the principle behind it.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThey still assert that conservatism is a social force reflecting a timeless understanding of how we live.

Political scale explained
Left wing votes are generally concerned with the principles of Socialism - that the state should work for the good of the people and which encompasses the ideas of democracy, free health care, the welfare state and some level of redistribution of wealth.
Further left than Socialism is Marxism, seeking to have the public in control of the economy rather than in private hands.
The idea is that instead of workers working for a private owner they work for a collective benefit that they can all share in.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdCulturally this further left position is concerned with the social responsibilities of the state to the individual and also of the individual to the state.
The extreme left is called Communism which propounds the idea of a society with no class boundaries where all citizens are equal with equal rights and opportunities.
The right wing are generally concerned with the principles of Conservatism which is a belief in upholding traditional established values.
Conservatism is built on the idea of a defined national identity and embraces a monocultural rather than a multicultural society.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdPolitical Conservatism is linked to the idea of Capitalism, the idea that the economy is strongest when based on competing factions, with wealth in the hands of the few used to employ the many.
Further right than Conservatism is Libertarianism, placing more emphasis on the individual’s rights than any obligation the individual has to community values.
Libertarianism is concerned with freedom and has become intrinsically linked to the concept of free speech.
The extreme right wing would be Political Fascism.
Fascism can be defined by the autocracy of a leader or government, a strong nationalist agenda and a pro-uniformity approach.
Diversity is not encouraged within a Fascist ideology, and there is great emphasis upon conforming to the unified goals of the state.
Comment Guidelines
National World encourages reader discussion on our stories. User feedback, insights and back-and-forth exchanges add a rich layer of context to reporting. Please review our Community Guidelines before commenting.
