Houthi rebels: who are the group in Yemen, why is UK involved after Red Sea ship attacks - where is Yemen?
and live on Freeview channel 276
Rishi Sunak has said the UK will "always stand up for freedom of navigation and the free flow of trade," following the Royal Air Force's targeted strikes against military installations used by the Houthi rebels in Yemen.
This is the first time strikes have been made against the group since it began attacking foreign ships in the Red Sea late last year, and it has threatened retaliation.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdUS President Joe Biden said that US military forces, supported by Australia, Bahrain, Canada, the Netherlands, and the UK, had successfully carried out strikes against several targets in Yemen.
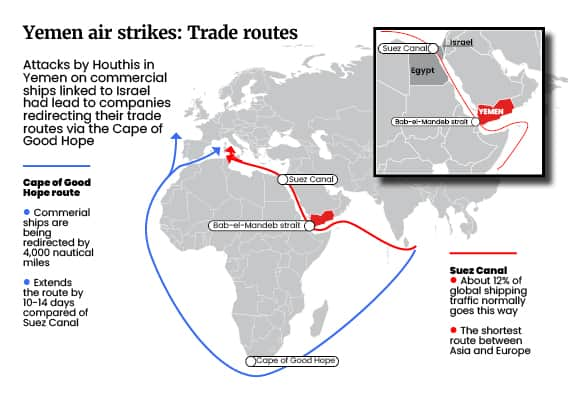
The Prime Minister said early on Friday (12 January) morning: “In recent months, the Houthi militia have carried out a series of dangerous and destabilising attacks against commercial shipping in the Red Sea, threatening UK and other international ships, causing major disruption to a vital trade route and driving up commodity prices.
“Their reckless actions are risking lives at sea and exacerbating the humanitarian crisis in Yemen. Despite the repeated warnings from the international community, the Houthis have continued to carry out attacks in the Red Sea, including against UK and US warships just this week.
But who exactly are the Houthi rebels, what exactly are their origins in Yemen, and what role have they played in the conflict? Here is everything you need to know.
Who are the Houthi rebels?
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThe Houthi rebels, officially known as Ansar Allah (Supporters of God), are a militia group that emerged in the northern part of Yemen. The group takes its name from its founder, Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, who started the movement in the early 2000s.
The Houthi movement originated in the Saada Governorate, an area in the northwestern part of Yemen, initially as a religious and cultural movement advocating for the rights of Zaidi Shia Muslims, who make up a significant portion of the population in that region.

The Houthi rebels follow the Zaidi Shia tradition, a branch of Shia Islam, and their movement initially aimed to address what they perceived as discrimination against their community by the Yemeni government.
They sought greater autonomy and better representation for Zaidi Shias in the political and economic spheres of the country. The Houthi movement gained momentum in the mid-2000s when their leader, Hussein al-Houthi, was killed by the Yemeni government.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThis event sparked a series of conflicts between the Houthi rebels and the Yemeni authorities. Over the years, the group evolved from a regional movement with specific grievances to a more formidable force with broader political ambitions.
One key factor that fuelled the conflict was the group's opposition to the Yemeni government's alliance with the United States and its support for the Saudi-led coalition.
The Houthi rebels perceived these foreign interventions as threats to Yemen's sovereignty and, in response, took control of the Yemeni capital, Sanaa, in 2014.
The Houthi takeover of Sanaa marked a significant turning point in the conflict. The group, now in control of the capital, further escalated tensions with the Yemeni government and triggered a series of events that led to a full-scale civil war.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdThe conflict has had devastating consequences for the Yemeni people, leading to a humanitarian crisis with widespread famine, disease and displacement.
Why are the US and UK getting involved?
The international community has been deeply involved in the Yemeni conflict. The Houthi rebels have received support from Iran, which shares a Shia Muslim affinity with the group.
On the other side, a coalition led by Saudi Arabia and supported by the United States has intervened in an attempt to restore the Yemeni government's authority.
The Houthi rebels have been accused of human rights violations, including indiscriminate shelling and recruitment of child soldiers. However, they argue that they are fighting against external interference and for the rights of their community.
Advertisement
Hide AdAdvertisement
Hide AdUS President Joe Biden has said the recent strikes were meant to demonstrate that America and its allies “will not tolerate” the militant group’s ceaseless attacks on the Red Sea. He said they only made the move after attempts at diplomatic negotiations and careful deliberation.
“These strikes are in direct response to unprecedented Houthi attacks against international maritime vessels in the Red Sea — including the use of anti-ship ballistic missiles for the first time in history,” Biden said in a statement.
He noted the attacks endangered US personnel and civilian mariners and jeopardised trade and added: “I will not hesitate to direct further measures to protect our people and the free flow of international commerce as necessary.”
Where is Yemen?
Yemen is a country located on the southern tip of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East. It is situated in Southwest Asia, bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, the Arabian Sea to the south, and Oman to the southeast.
Yemen has a diverse geography that includes mountains, deserts, and a coastline along the Arabian Sea.
Comment Guidelines
National World encourages reader discussion on our stories. User feedback, insights and back-and-forth exchanges add a rich layer of context to reporting. Please review our Community Guidelines before commenting.
